CRM KPIs (key performance indicators) are essential tools for businesses that want to measure and improve their customer relationships. These metrics allow businesses to track the effectiveness of their customer relationship strategies, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions about how to allocate resources. In this article, we discuss the usefulness of CRM kpi’s and which indicators are most important. Of course, we provide CRM KPI examples to give you a quick start! Let’s go!
What is a CRM KPI?
CRM (customer relationship management) KPIs (key performance indicators) are metrics that help a business measure the effectiveness of its customer relationship strategies. These KPIs can be used to track the progress of the business toward its customer relationship goals, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions about how to allocate resources.
Most companies do work with CRM KPIs. Even if they don’t name it as such. The most important metrics for commercial departments are included in CRM KPIs.
Examples of CRM KPIs
Some examples of CRM KPIs include:
- Customer retention rate: The percentage of customers who continue to do business with the company over a given period of time.
- Customer satisfaction score: A measure of how happy customers are with the products or services they receive.
- Lead conversion rate: The percentage of leads (potential customers) that are successfully converted into paying customers.
- The average revenue per customer: The amount of money that a business earns from each individual customer over a given period of time.
- Customer acquisition cost: The cost of acquiring a new customer, including marketing and sales expenses.
By tracking these and other KPIs, businesses can optimize their customer relationship strategies and improve their overall performance.
These are the most commonly used CRM KPIs
There are endless KPIs to consider if you want to measure commercial success. That is not to say they are all equally relevant or important. Nor is it workable to work with many targets and metrics. In general, it is wise to use only a handful of CRM KPIs. This will help you keep an overview, keep everyone on track and make it clear to everyone what needs to be worked on.
Some of the most important CRM KPIs with examples:
1. Customer Retention Rate
One of the most important CRM KPIs is the customer retention rate, which measures the percentage of customers who continue to do business with the company over a given period of time. A high retention rate is a sign that the business is providing a high level of value to its customers, and it is typically a good indicator of overall customer satisfaction.
Let’s look at a practical example with this KPI
An office furniture supplier manages this KPI and notes that most customers are using its maintenance services for six months or less. However, a benchmark with other companies in the same industry shows that this is on the low side. Most competitors retain customers for two years or more. A clear deviation from the average could be investigated. Perhaps the service does not match the market? Or is there something missing in the communication that makes customers more likely to walk away? Whatever it is; by focusing on this, you can act on it.
2. Customer Satisfaction Score
Another important CRM KPI is the customer satisfaction score, which measures how happy customers are with the products or services they receive. This score can be obtained through surveys, focus groups, or other methods of gathering customer feedback. A high satisfaction score is a sign that the business is meeting or exceeding customer expectations, and it can help to improve customer loyalty and retention.
Let’s consider the example of a tech startup that received a dismal satisfaction score for its new mobile app.
Rather than ignoring or dismissing the negative feedback, the company’s management embraced it as a chance to understand their customers better. They delved deep into the feedback, identifying recurring issues and pain points that users faced. Armed with this valuable insight, the development team swiftly began working on updates and enhancements to address those concerns. Through transparent communication with users and proactive measures, the startup was not only able to regain customer trust but also turn the situation around, eventually leading to an uptick in customer satisfaction scores. This example illustrates the power of embracing customer feedback and using it as a catalyst for positive change, ultimately paving the way for sustained success in the future.
3. Leads
When we look at new business targets, the number of sales opportunities or leads often are the most important.
Leads are potential customers who have expressed an interest in a company’s products or services. These individuals may have filled out a form on a company’s website, signed up for a newsletter, or otherwise provided their contact information.
Top-of-funnel leads
For businesses, leads and sales opportunities are valuable because they represent an opportunity to convert these individuals into paying customers. To generate leads, businesses often use marketing tactics such as content marketing, events, and email marketing. Once a lead has been generated, it is typically the responsibility of the sales team to follow up and try to convert the lead into a paying customer.
To be effective, businesses must have a clear process in place for managing and nurturing leads, from the initial point of contact to the final sale. By converting leads into customers, businesses can drive revenue growth and improve their overall performance. Building an effective lead generation and conversion process can be done with marketing funnels.
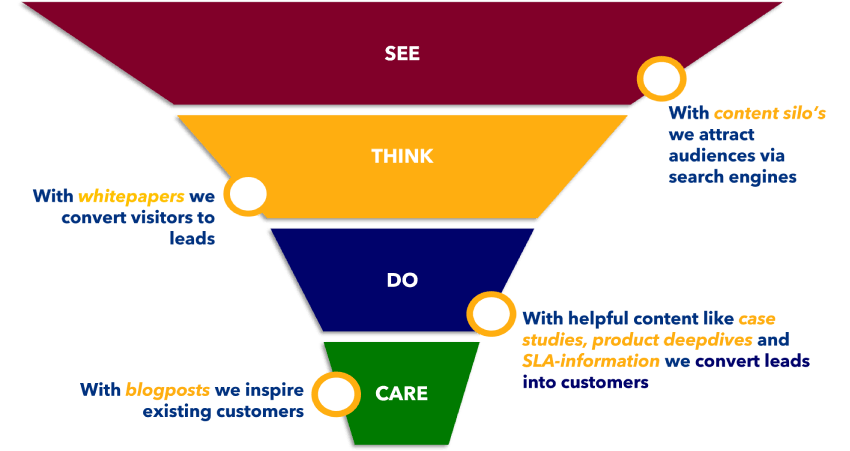
CRM KPI Example from my own experience: how to respond to a dearth of business leads
In the dynamic world of business, new leads are the lifeblood that sustains growth and prosperity. However, what happens when the flow of fresh leads begins to slow, leaving your sales team with a sense of frustration? One company I worked for in the past, faced precisely this challenge when we noticed a decline in new business leads for our software services.
Instead of succumbing to despair, we chose to view this as an opportunity to refine the lead generation strategy. We reevaluated the target audience, made choices about who we no longer saw as a communication target group (focus), honed in on the pain points that truly mattered to this specific group of potential clients, and crafted personalized outreach campaigns. Content marketing and online marketing were leading in this strategy.
Additionally, we ramped up the presence on social media platforms, engaging with followers and establishing our experts as thought leaders in the industry.
The result? A revitalized lead pipeline and a stronger brand presence.
Check out our top 3 CRM solutions that excel in driving Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
4. Lead Conversion Rate
The lead conversion rate is another important CRM KPI. This metric measures the percentage of leads (potential customers) that are successfully converted into paying customers. A high lead conversion rate is a sign that the business’s sales and marketing efforts are effective, and it can help to drive revenue growth.
An example of this CRM KPI in practice
This is a hot topic right now. Companies generate many leads (email addresses) from the potential buyer but they just don’t convert them to hot leads or customers.
This can have many causes. The most likely is the intention of the contact in relation to the action taken. Did someone download your whitepaper? Super! However, that does not immediately mean that there is a project running for which you will be shortlisted.
In this particular example of dealing with CRM KPIs, it is important to look beyond and take the potential customer by the hand for the longer term. Then, should a project go ahead, your organisation will be top of mind and you can still expect a conversion.
5. Average revenue per customer
The average revenue per customer is another key CRM KPI. This metric measures the amount of money that a business earns from each individual customer over a given period of time. By tracking this metric, businesses can identify opportunities to upsell or cross-sell to their existing customer base, and they can also identify opportunities to improve the value of their products or services.

Example with this CRM KPI: Navigating Low Average Revenue Per Customer
A good average revenue per customer is the bedrock of financial sustainability and growth. The cautionary tale of VanMoof, a renowned Dutch e-bike manufacturer, serves as a stark reminder of this vital aspect. As a scale-up company, VanMoof faced a challenging situation where the cost of manufacturing their innovative e-bikes exceeded the revenue they generated from sales.
Despite gaining popularity and a loyal customer base, the company struggled to strike a healthy balance between production costs and pricing. As a result, they found themselves unable to meet their financial obligations, leading to their unfortunate downfall and eventual bankruptcy.
This tale underscores the importance of setting appropriate pricing strategies and understanding the value your product or service brings to customers. A robust average revenue per customer ensures that your company can cover its expenses, invest in research and development, improve customer experiences, and ultimately remain competitive in the market.
For businesses aiming for sustainable success, analyzing and optimizing average revenue per customer should be a top priority. By understanding the cost structures, value propositions, and competitive landscape, companies can make informed decisions about pricing, product development, and overall profitability. The story of VanMoof serves as a poignant reminder of the consequences of overlooking this crucial metric and emphasizes the need for a vigilant approach to financial management in any enterprise.
6. Customer acquisition cost
Finally, the customer acquisition cost is an important CRM KPI that measures the cost of acquiring a new customer, including marketing and sales expenses. By tracking this metric, businesses can identify the most cost-effective ways to acquire new customers and optimize their marketing spend.

Navigating high acquisition costs per customer: learning from the story of a meal kit service
In the realm of business, customer acquisition is a fundamental goal for any company seeking growth and success. However, when the cost of acquiring new customers becomes prohibitively high, it can become a challenging roadblock to sustainable profitability. A vivid example of this can be seen in the case of a healthy meal kit service that offered nutritious and convenient meals delivered to customers’ doorsteps. Despite providing a high-quality product and investing heavily in marketing campaigns, the company struggled to keep the acquisition costs per customer in check.
Rather than ignoring the issue or succumbing to defeat, the founders took a proactive approach. They delved into their CRM KPI analytics to identify the most effective customer acquisition channels and optimized their spending accordingly. Additionally, they focused on customer retention and referral programs to capitalize on their existing customer base. By offering incentives for loyal customers to refer friends and family, they were able to acquire new customers at a fraction of the previous cost.
Through dedication and strategic thinking, the mail kit service company transformed its high acquisition cost challenge into an opportunity for innovation and growth. By continuously monitoring and adjusting their marketing strategies, they were not only able to reduce customer acquisition costs but also build a strong community of satisfied customers who became brand advocates.
This example highlights the importance of being proactive, data-driven, and customer-centric when faced with high acquisition costs, as businesses can uncover hidden potentials and ultimately achieve long-term success.
Your CRM KPI-dashboard is essential for this.
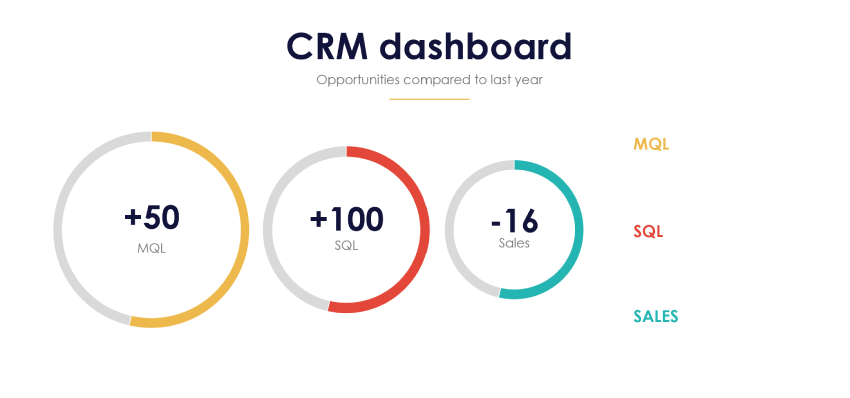
Implementing CRM KPIs
Installing customer relationship management key performance indicators is an important step for businesses that want to measure and improve their customer relationships.
1. Identify metrics and objectives
To be successful, businesses need to first identify the specific metrics that are most relevant to their goals and objectives.
This may involve consulting with experts in customer relationship management, studying industry benchmarks, and gathering input from key stakeholders. And reading the articles on crmreviews.com of course! 😉
2. Select CRM Software
Once the appropriate KPIs have been identified, businesses can then choose a CRM software or platform that allows them to track these metrics in real time. This software can be customized to fit the specific needs of the business, and it can be used to generate reports and analyze CRM data to help inform decision-making.
Check the dashboard in your CRM software. Is it able for tracking the most important KPIs?
3. Use KPIs for improvement
By installing CRM KPIs, businesses can gain valuable insights into their customer relationships and take action to optimize their performance. Every CRM strategy should start with identifying the metrics that are going to be used to measure the performance of the organization.

Sales Rep CRM KPI Example
The most practical KPI’s we see in sales teams everywhere are those metrics that follow the customer journey. For example: How many marketing leads did you receive from marketing? How many hot prospects did you manage to generate? How many sales opportunities are currently in your pipeline? And so on.
These dashboards are often used in sales meetings to measure progress.
In dit table you find an example:
| Sales Rep | MQL | SQL | Opportunity | Closed Deal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| John Carter | 200 | 35 | 11 | 5 |
| Eline Boss | 175 | 20 | 9 | 6 |
| Carry White | 225 | 13 | 15 | 5 |
What CRM KPIs are you working with? And do you have examples for us?
Overall, CRM KPIs are critical tools for businesses that want to improve their customer relationships and drive long-term success. By tracking these metrics and using them to guide decision-making, businesses can optimize their customer relationship strategies and achieve their goals.
Check out our top 3 CRM solutions for this month
Recommended Reading
Essential CRM data for every business
But what you may not know is that your CRM data can actually be a valuable asset for your business. How do you keep your data up to date?
Direct Marketing
Direct Marketing, the defenition and strategies to be successful with it in combination with CRM. Read our tips!
Quotation tips that will increase your scoring rate in 2025!
With these quotation tips, you will increase your scoring chances straight into 2025! Turn your quotation into a sales tool. Read more...
Customer Journey: a definition and more!
The Customer Journey refers to the path a prospect takes before making a purchase decision. Learn from our insights and examples!
What are the benefits of CRM software?
What are the benefits of CRM software? Learn what CRM systems can do for your business and how you profit form the benefits
Unveiling the AI revolution in CRM: 7 applications redefining business dynamics
Unveiling the AI revolution in CRM: 7 applications redefining business dynamics. How AI can help your business.
