A Customer Relationship Management strategy is a plan that describes how the relationship with customers (and prospects) is maintained. The basic principle here is usually to optimally serve customers and prospects in the most efficient way possible.
Okay, that’s the definition. But what is the position of Customer Relationship Management in your organization? Drawing up a CRM strategy can help you make the right choices regarding prospect and customer contact. In these articles we dive into the world of CRM and we look at how you determine a CRM strategy and what it involves.
Why do I need a CRM strategy?
It is generally believed that a good CRM strategy can lead to higher customer satisfaction, more leads and more sales. (Also read this Forrester article on the benefits and trends for 2020).
The CRM vision is based on capturing the right information from prospects and customers in order to be able to serve them as well as possible. And thereby increase the success of the organization. Where CRM was originally mainly a digital card index to support the sales team, we now see applications for the entire organization.
CRM for the entire process
Modern CRM systems with an extensive module structure provide support for many processes. From marketing (crm for marketing) to sales, from project management to service. Systems that focus on ZZP and SME often also provide for the generation of quotations and the final handling of an entire customer process with invoicing and after-sales functions.
Back to strategy. The success of a CRM strategy naturally depends on its implementation. Making plans is fun, but a CRM strategy also includes a CRM tactic and a good operational rollout. A determining factor in this is the appropriate tooling. Then it is about choosing a good CRM system that is subservient to the CRM strategy.

What will my company look like without a CRM strategy?
A focus on managing customers, or rather; customer contacts are intensive and require an investment. Thinking about a CRM strategy is not a priority for every organization. In certain cases, the organization is especially ready for the next step in centrally recording and managing customer and prospect information. Another growth phase may require a deepening of the CRM idea within the company.
You can choose a minimal CRM strategy based on a background role for the CRM system or a strategy based on an extensive customer view.
1. A minimalist CRM strategy
A thought can be;
When it comes to digitally capturing data, I purchase a CRM system and fill this system with the absolutely necessary data. My vision on CRM is simple because in this organization the focus is on operational excellence. Moreover, our market is small and every customer knows us.
The question is what exactly you are going to record and what you are going to do with that data. But even if that is little, that is also a CRM strategy. Namely: with minimal effort and the recording of basic database data, it is easier to keep track of and consult customer information.
Digital card box-plus…
In this case, the database serves purely as a digital card index with master data. There is a good chance that this does not contain any data such as the customer’s previous activities or preferences. Then you have a CRM strategy that is aimed at a minimal customer information focus. It is possible that the customer information is there, but that it is only available in the mailbox and the heads of the account manager.
The downside of this is that marketing has to segment based on minimal data, much depends on the Account Manager’s knowledge of certain customers. And that there is less redundancy; if you work together on a customer project or the account manager drops out, no knowledge about the project or customer is recorded.
2. CRM strategy based on 360 degree customer view
A CRM strategy based on centrally building a database based on a complete 360-degree customer view has been expanded. This strategy is based on a customer-oriented approach in which CRM forms the basis for the marketing and sales efforts. This strategy is based on the optimal use of data in order to connect as closely as possible to the customer journey of the target group.

A lot of attention is paid to maintaining the database and several functions of the systems are used to take advantage of the possibilities as much as possible.
This strategy also has drawbacks. For example, it takes a lot of work to create, fill and maintain such a database. People from different departments also have to learn to work with the system and follow procedures. This is not only about working in a tool, it is also about the vision on customer focus and how this vision is propagated.
Position of CRM in the company
A CRM strategy, therefore, determines the way in which customer contacts and customer data are handled. The strategy also answers the question; what is the position of CRM in the company and what do we agree on about this?
Every company has some kind of CRM strategy, although this is not always recorded as such. The way in which the customer journey is handled has been considered and a plan has been drawn up for the optimal design of the organization around the touchpoints in this customer journey.
You can also include in the plan how you will realize the most value from the database and translate customer insights into;
- product development,
- marketing and sales campaigns,
- setting up the service organization.
In the process of determining the CRM strategy, questions such as:
- what do you expect to get out of the focus on customer relationship management?
- What if you don’t change anything?
- Where are the opportunities that you are not currently taking advantage of?
- How can you benefit from the use of a CRM strategy?
- Where is the initiative?
- How do you measure your CRM strategy? What CRM KPIs are essential?
Where does a CRM strategy belong?
A CRM strategy is a central element of the entire organization. So there will have to be support from the management. In addition, it is a broad vision of dealing with customers and relations. A broad delegation will therefore have to be involved.
CRM is NOT a celebration of Marketing.
Not even from Sales.
Or Service.
And certainly not just from ICT.
Working according to a customer relationship management strategy requires the participation of multiple disciplines. In many cases the same degree of impact, depending on the objectives.
Ambassadors of the CRM strategy
The project can be driven by a certain discipline. Think of Marketing as a driver for a CRM strategy. The focus on customer relationship management and the use of CRM software can be a wish born of an opportunity, supported by a business case.
But even though Marketing is the driving force behind the project; it will hit multiple departments at the heart of the operation. Involving the right departments in the early stages of the project is therefore decisive for its long-term success.
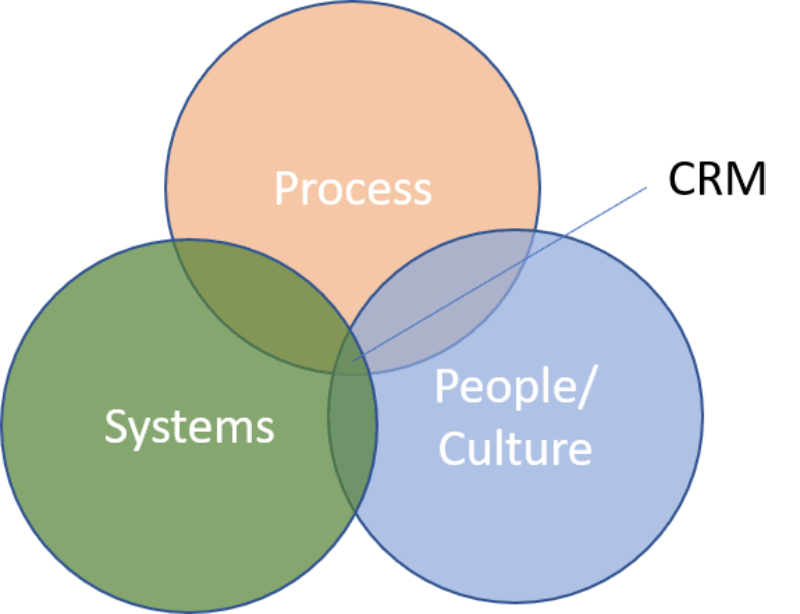
A CRM process is always an interaction between:
- Technology (CRM software and other related tools)
- Processes (what are you going to do and how will you set up?)
- People/culture (which people will work in which way with the software. Is there a customer-oriented culture? Or is there a process-oriented culture based on operational excellence?)
An example of coherence in a CRM strategy:
Marketing would like to focus more on customer relationship management and will use CRM software to build the prospect database. This database forms the basis for marketing campaigns. Central to this are email newsletters.
The idea is on the one hand to add value with informative content and on the other hand to roll out concrete offers and event invitations via the CRM database. As soon as a prospect takes an action, it is the intention that sales will continue to work with it. In this example, it is very important that there is good cooperation between marketing, sales and ICT. The system must support the processes and the people must be able to work with it in a pleasant way. E-mail marketing and CRM need to be well coordinated.
If there is a mismatch in this and this is not based on the same CRM strategy and associated tactics and systems, things will go wrong. The prospect suddenly experiences a different type of contact and notices that Sales has no idea about the previous marketing process (and the information that has already been sent to the prospect).
What does a CRM strategy consist of?
A CRM strategy describes the position of the prospect and customers in an organization. This is based on a vision that is translated into a concrete goal. This is translated into the previously discussed three-way division of technology, processes, and people. Not only does this contain a vision of customer focus, but also very concrete matters that have an impact on the organization. Some sample questions to consider:
1. Technic
With which tools are we going to store, process and use our CRM data? How is the CRM software related to other tools in the organization?
2. Processes
Where does the responsibility for the prospect database lie? Where does the responsibility for customer CRM data quality lie? How are contacts recorded in the systems? What is automatic and what requires human action? In what way does CRM get a role in other processes such as those of the service department?
3. People
Who will enter, edit and use data in what way? What does the rights structure of the licenses look like? How will people get to know the system and be trained in it?
Tip! Create a CRM roadmap to make the CRM strategy more visual within the organization!
Which tools are part of your CRM strategy?
An important part of the CRM strategy is the choice of software. Which tools will you use to shape customer relationship management within the organization? Here are a few important things that we were able to read earlier in this article: Selecting CRM with concrete tips.
Wide landscape
The CRM landscape is vast and tools differ in many ways. There are a large number of players in the market. One focuses on the full automation of a business process. The other is purely on the sales process. There are big players and small but very specialized players.
There is also a visible development of software solutions that will enter the CRM market by adding functionality. HubSpot is an example of this. This marketing automation tool also added CRM functionality a while back.
CRM strategy funnels
Part of the crm strategy are funnels. These are different contact strategies based on the customer journey of the target group. By setting up multiple funnels, customer contact can be automated. Of course, this can be controlled from CRM software in combination with other tools. Some examples of funnels for your CRM strategy are:
- upsell funnel
- lead nurturing funnel
- event/webinar funnel
A CRM strategy checklist
Finally, a number of handy boxes to tick when it comes to setting up and rolling out a CRM strategy. You probably don’t spend every day setting up a CRM strategy. You can always get help from a CRM expert. A few points that you may not immediately think of or steps that are easily skipped:
✅ Are the key players involved? So they represent IT, Marketing, Sales, Service and the most important key-users?
✅ Has the strategy been drawn up SMART? Is there agreement on the goals and preconditions? Can the CRM strategy be compared to the three pillars: Technology, Processes, and People?
✅ Is it clear who and what is needed to roll out the strategy?
✅ When are evaluations scheduled?
✅ Has change management been considered?
✅ When is the CRM strategy a success?
Looking for a new CRM solution? Try our widget and make your CRM comparison.
Also check out our article on free crm!
Check out our top 3 CRM solutions for this month
Recommended Reading
The Guide to Successful CRM Deployment: Best Practices and Key Steps
In this blog article, we will explore the key steps involved in CRM deployment and some best practices to ensure a successful implementation.
Sales qualification standard: BANT
What is BANT in relation to marketing and sales and how do you use it in your CRM? Read our insights on this topic!
The importance of creativity in B2B marketing: the relationship between innovation and growth
The importance of creativity in b2b marketing is often underrated. With this article i show the benefits of creative marketing!
AI and CRM: how artificial intelligence is reshaping the future of customer relationship management
AI and CRM: How artificial intelligence is reshaping the future: relationship management is never going to be the same
CRM for Marketing: 9 tricks for marketers to get more out of CRM in 2024
CRM for Marketing: 9 tricks for marketers to get more out of CRM in 2024: tips to get the most out of your CRM as a marketer
Finding the Right CRM Expert for Your Business: Tips & Strategies
The role of CRM experts, tips and steps for businesses to find and select the right expert to help them with their CRM strategy & deployment.
