CRM (Customer Relationship Management) is a vision in which the customer relationship is central. By knowing the shes and needs of the customer. CRM software or CRM systems support Sales and Marketing in this. In practice, people often talk about CRM when it actually concerns CRM systems. In this article, we dive deeper into the theme and you learn all the ins and outs.
What is CRM?
CRM is a business strategy aimed at establishing, maintaining and expanding customer relationships in a way that creates value for both the company and the customer (Beltman, Peelen and Waalewijn, 2000).
This is a definition of CRM, but there are others. Most definitions do contain a number of similar parts:
- It’s about putting the customer first
- It is a strategic method, a business strategy
- CRM aims to increase revenue and profits by attracting new customers and increasing customer satisfaction
- It is a software based strategy in order to optimize business processes and save costs
- With CRM organizations pursue a win-win situation where customers and the organization achieve a better situation
In practice, we see different applications of CRM and interpretations. In some cases it is no more than a glorified card catalog, in other cases, CRM forms the core of organizations and their commercial strategy. Now that this strategy and associated software have been used for so many years, we are also seeing new insights into the subject. Many organizations see CRM as:
- Business strategy with a focus on achieving long-term goals and generating competitive advantage.
- Marketing vision with a focus on the wishes and needs of the customer in combination with the goals of the organization
- Change process to a customer-oriented organization
This is one of the fastest-growing businesses in the world. Estimations are that the market will be as big as 42.41 bn dollar in 2024.
CRM providers
There are many CRM software packages and CRM system providers in the world. We see SAAS providers, offline providers, CRM service providers, CRM as part of accounting software or ERP systems.
An overview of a number of commonly used CRM solutions for the self-employed and SMEs can be found here.
- Monday CRM
- SalesForce CRM
- HubSpot CRM
- Microsoft Dynamics CRM
- Pipedrive
- Salesflare
- Gripp
- Zoho CRM
A number of solutions lined up, divided over a smaller number of users (SME) and a larger number of users (SME/Enterprise).
1) CRM for SME
- FunnelCRM
- Salesflare
- Pipedrive
- ZOHO CRM
- Freshsales CRM
- Suger CRM
- V-Tiger
- Hubspot CRM
- Monday CRM
- SCORO CRM
2) CRM for Enterprise companies
- Microsoft Dynamics CRM
- Sage CRM
- SalesForce
- PerfectView CRM
- Super Office
On this site, we look at the trends in CRM and we highlight different sides of this customer strategy and associated systems.
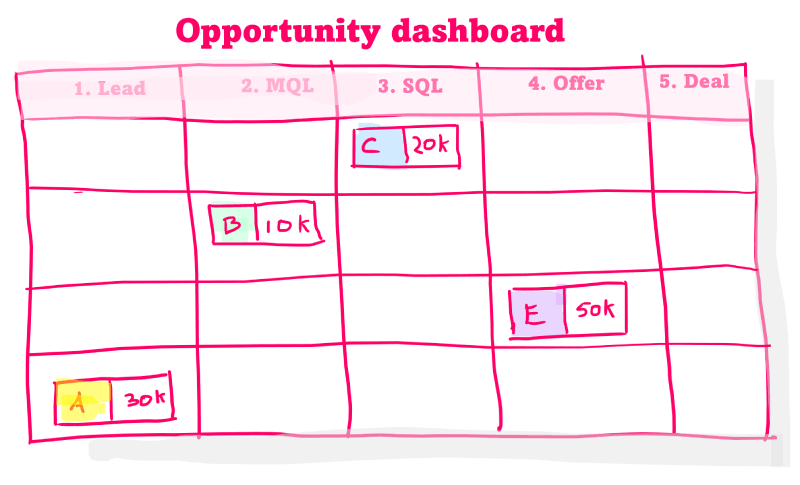
Okay, so what do I need a CRM for?
CRM software or a CRM system is a tool for sales and marketing to manage relationships and sales opportunities. Company and contact details are stored in the system with links to; interactions, sales processes and other data aimed at managing and editing prospects and leads.
It is more than a glorified card catalog; the CRM database is a very valuable asset for many companies.
This makes it one of the most important tools for the B2B marketer, account managers, new business sales professionals, commercial managers and executives. People also talk about a CRM package, CRM solution or relationship management system. CRM in marketing is one of the pillars of modern marketing departments.
So, are you investing in marketing funnels or working on your account based marketing strategy? In both cases this kind of tooling is essential to get results.

Personal note 😉
I have been working in the world of b2b marketing for more than 15 years. Both on the agency side and the client side, I have seen how important these kinds of tools are for commercial strength. Without CRM, a marketing or sales department is paralyzed. Also, when it comes to cooperation between marketing and sales, tools like this have a bridging function.
There is an explosion of tools around sales and marketing; by far most are nice-to-haves where customer relation ship software really belongs to the heart of the marketing and sales department.
CRM systems on the rise
The number of CRM Systems has grown enormously in recent years and the category is still growing. On the one hand, this growth can be explained by technical progress and expansion of functionality.
On the other hand, more and more companies are realizing that this kind of tooling can help them optimize the sales and marketing process. There are more and more CRM system suppliers that focus on different niches in the market.
What does a CRM system cost?
The costs of CRM systems vary from 8,- per user per month to 300,- per user per month. The costs depend on a number of factors and are also calculated in different ways. A number of variables are included here:
On premise of SaaS solution
The world of online software (SaaS) is booming. Yet there are still packages that work according to an on-premise model. Which means; the software is implemented locally on the company’s server, for example, and cannot be accessed via a general cloud environment. Most CRM systems today are available SaaS, so as a software product that you approach as a service; then you pay a price per user per month to use the tooling.
The variables to determine the costs are then:
- Number of users (the more users of the system, the higher the costs)
- Pay per month or per year (often suppliers give a discount on the monthly costs if you pay per year)
- Database size charges (there are systems that charge additional fees as the number of records in the system increases)
- Functionality (prices are determined depending on the desired functionalities for certain users. These are, for example, extended licenses. It also happens that certain ad-ons or apps can be added as a supplement to the CRM system. Then companies pay for this. can also be third party apps from a marketplace.
- Initial costs (some suppliers charge one-time costs for on-boarding or provisioning the system)
- Consultancy costs (CRM suppliers can provide additional services for setting up the system, reading the database or building functionality).
- Service costs (related to the consultancy costs, there are systems that offer extra service levels for a fee. In that case, for example, you get priority over the service desk. This can be recorded in a Service Level Agreement (SLA)
- Training costs (there are providers that can help you with training to get more out of the system. This can also be professional training and training that can be followed for a fee.
- Additional costs (also take into account other costs that may become relevant such as integration costs of the current CMS party or the e-mail marketing partner. The integration of the CRM system with this type of software can also cause additional costs from the existing suppliers.
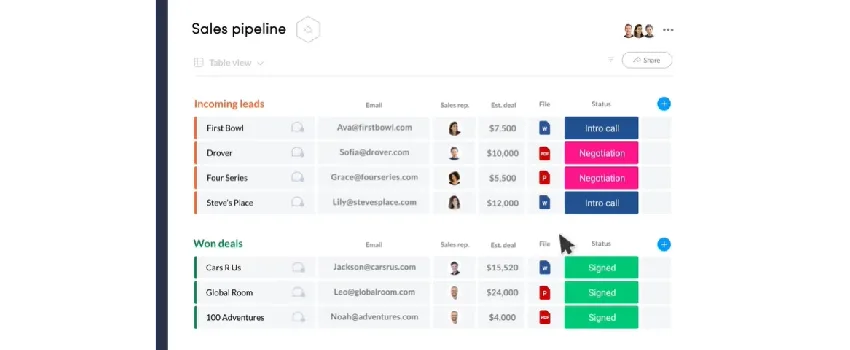
How does CRM work?
CRM is based on a database that is constructed in different ways. With this data, employees are able to organize the marketing, sales, and service process more efficiently and better. The software makes connections between data, offers reports, provides notifications and alerts, and automatically takes actions.
For example, if an opportunity is moved to another phase, tasks can be automatically placed in an account manager’s calendar or emails can be sent.
The data can be entered into the system in different ways:
- Salespeople, back office employees, service employees, account managers and marketers enter data into the CRM system. This further enriches the database.
- Data is automatically loaded from database suppliers such as the Chamber of Commerce.
- Data is enriched with data from Social Media platforms such as LinkedIn
- Data from external systems such as email marketing software enters the CRM software via a link
- Data is entered from forms on websites
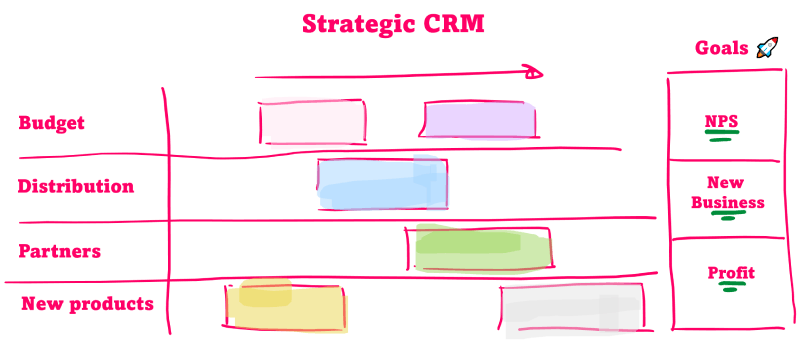
A CRM strategy, how do you approach it?
Customer Relationship Management is a vision of dealing with organizational relationships. It is wise to draw up a CRM strategy and make a plan for its rollout. This type of strategy belongs at the heart of the organization and does not only embrace the marketing or sales departments. It is therefore recommended to incorporate the insights of multiple disciplines. Depending on the level of ambition, an investment in CRM software is an essential part of a successful rollout. But it is more than software. You can use the following model to shape the CRM strategy:
- Technic
- Processes
- People/culture.
if you have set up a CRM strategy, it is important to share it with the organization in an understandable way. You can choose to create a CRM roadmap. Hanging it up as a poster throughout the organization will immediately make the project more alive among employees.
CRM system as a digital card index for marketing & sales?
By building a good database and recording customer knowledge, effective, targeted marketing campaigns can be realized. In this way, the mix of resources, message, and contact frequency can be optimally tuned to the target groups. Today’s CRM software systems offer extensive possibilities and have long and broadly outgrown the character of the digital card index.
CRM functionalities sales and marketing
A CRM system is a complete solution for total Marketing, Sales and Service support. Think of marketing and sales functionalities such as;
- target audience segmentation,
- opportunity management,
- email marketing,
- campaign management,
- document management
- service management
Within the CRM world, a lot of attention is paid to providing management information and integration with other systems.
So there are also CRM systems that go much further and cover an entire business process. Teamleader, for example, is strong in covering a large part of the business process of smaller organizations. But the larger packages such as SalesForce also offer very extensive functions to support the sales and marketing department. But a system like ActiveCampaign also excels in email marketing, Marketing Automation and Relationship Management.
What should you pay attention to when comparing CRM systems?
Because the CRM system forms (or will form) the heart of the commercial organization, it is important to carefully consider a number of things. Below we discuss a number of important points for attention in addition to the obvious standpoints (such as price).
1) Current software landscape of your organization
When comparing CRM systems, you cannot ignore the current ICT spectrum. If several software products are already in use that are related in a certain way, this can be important when considering a new CRM system.
Integration into current IT landscape
Most CRM packages can be linked to other systems to a greater or lesser extent, but these are not always the best connections. For example, if you have a strongly Microsoft-oriented IT landscape, a choice for Microsoft Dynamics 365 CRM could be a logical one.
And otherwise, take a good look at the extent to which the possible CRM solution fits in with that landscape by paying a lot of attention to the available APIs, apps and other connection options. This can save you a lot of frustration later on.
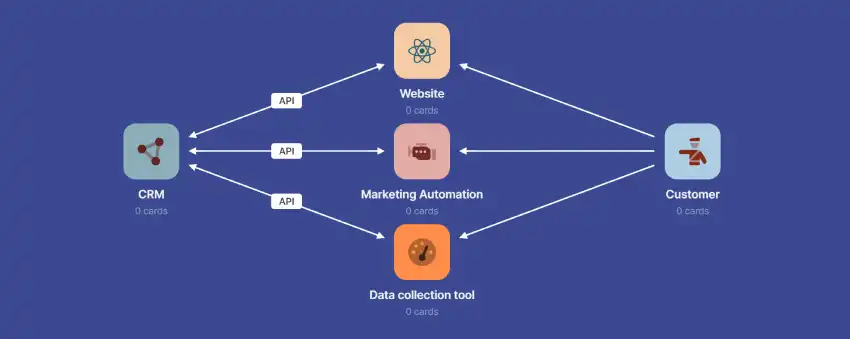
In addition to the choice of platform, it can also be important which functionalities are already present. So which processes are already covered? For example, is there a powerful email marketing package in use? Then this functionality does not have to be in the CRM system, but then a good connector is of great importance.
Only by making the systems work well together can you achieve maximum returns with the entire software landscape.
2) Support and consultancy ☎
Good support, documentation and a strong help desk can make the difference between a successful CRM implementation and a failed one. New wishes can also gradually arise and new people start working with the system, so that solid support can play an important role in the choice for a CRM system. Every organization is different in this regard. To what extent the support is in line with the organization is really something you have to find out for yourself.
There are CRM suppliers that provide Dutch support and are even of Dutch origin (Archie CRM, PerfectView CRM). This can be an advantage for many organizations when comparing the right CRM system. Foreign CRP systems often have Dutch implementation and consultancy partners.
3) Organizational growth ambitions
Another important factor that is often overlooked is the expected growth of the organization. A fast-growing club with a heavy commercial focus could benefit from a system that works well with smaller companies as well as larger companies such as SalesForce CRM. A company that expects to stay small and not expect very rapid growth might be better off with a CRM system that fits best like Pipedrive CRM.
4) Functional options of the CRM package
One of the most important deep dives you’ll make when comparing CRM systems is the functional breadth and depth of the package. A package such as Teamleader is very broad in terms of functionality and can cover a large part of the business processes. A package like Pipedrive is more of a best-of-breed solution that focuses strongly on CRM functionalities. Here too it is wise to look at the growth ambitions and the total ICT landscape at the organization.
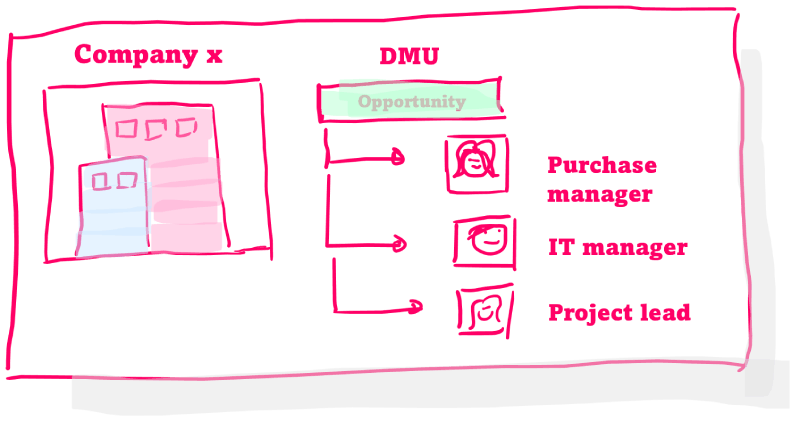
Features of CRM Systems
What are the common features of CRM systems now? There is a huge proliferation of tools in CRM land with all different functions. Common features include:
- Business and contact details; This contains information about the accounts and the associated contacts. Information is often kept here such as: company name, location, relationship to holding/group, website, business activity, sector description, SIC code, Chamber of Commerce number. The companies include various contact persons whose CRM data is kept such as; name, role, contact details, social media profiles, interaction moments, place within the DMU.
- Opportunity Management; this is where sales opportunities, possible orders or projects are recorded. These are linked to the companies and often include; order value, chance of success, project or product type, expected order date, stage in the sales process.
- Reports and Analytics; overviews of certain steering information can almost always be found. For instance; the number of sales opportunities per seller, the number of closed sales opportunities in a year, the number of contacts within a specific target group, the number of interaction moments within a specific segment.
- Segmentation capabilities; Most SMB and Enterprise CRM systems provide segmentation and filtering capabilities. This makes it possible to perform analyzes and to compose target groups for sales and marketing campaigns. For example, a list can be made of contacts with a specific function who work at companies of a certain company size in a certain region.
- Options for interaction: more and more CRM systems offer options to apply email marketing from within the CRM system. By calling an email marketing engine from within the CRM package, direct marketing messages can be sent from a segment in the CRM system. This can also take place through an integration with an external e-mail marketing system. There is often also a link between the CRM package and the e-mail client that is used, such as Outlook. This enables salespeople to send direct mails from the CRM system to prospects and customers.
- Task management; a feature common to many CRM systems is task management. This allows you to assign tasks to people around a relationship card or opportunity. In most systems you can assign individual tasks to people or assign tasks in bulk. This comes in handy when monitoring a campaign, for example. With this you can, for example, have a selection of companies that have received a mailing followed up by an account manager. Users can also assign themselves tasks. An example of this is scheduling a task to follow up a sales call. Most CRM packages have capabilities to work with tasks or actions.
What are the benefits of CRM?
By focusing on Customer Relationship Management and working with CRM software, companies can work on the market more effectively and efficiently. By recording and applying the right data in marketing, sales and service activities, you can speed up and improve processes. A number of concrete benefits of CRM:
- Collaborate more efficiently:
Relevant customer information is no longer just in people’s heads, but is also embedded in the systems. Several people can request information and thereby serve prospects and customers. - Smarter Marketing:
By capturing the right data, marketing can build segmented campaigns to inform customers and convert prospects. - More effective sales companies:
Sales professionals keep a grip on their pipeline and can work systematically on winning new orders. Customers can be provided with the right information at the right time. - Better management by data:
Management and management have insight into the expected turnover and can make well-founded decisions based on the market information from the CRM database. Think about decisions about; tapping into new markets or developing new products and services. - Keep customers longer:
With more insight into customer needs, organizations can respond better to this. CRM systems are designed to record valuable information for this purpose.
Reed this article for more about CRM benefits.
What are the disadvantages of CRM?
The degree of customer focus and marketing differs per company. There are companies that have less need for rich-filled CRM systems. There are companies that only work for a few customers and know them very well. They may benefit less from an extensive CRM system. The focus can also be on other areas.
Let’s take a look at the disadvantages of CRM:
- The systems can be pricey, depending on the database size, number of users and functionality offered.
- Working with CRM systems requires an adjustment of the people within an organization. A lot of data will also have to be recorded.
Management Information & dashboards in Customer Relationship Management
Due to the amount of information that can be recorded, CRM software offers an interesting source of management information. By analyzing customer data, plans can be made for target group choices and contact strategies. An important part of this is recording and monitoring sales opportunities. By dealing with this accurately and in a disciplined way, predictability increases considerably.
What is CRM for management?
Management information can be displayed in different ways. For example, through reports in the CRM software, KPI dashboards or analysis dashboards from other tools such as Power BI. For Marketing, Sales and Services, CRM tools provide management insights and often provide the most important management information for the MT meetings.
Pipeline order value
CRM is therefore one of the most important sources for management across the board. It is the go-to system from which you can deduce what revenue the organization can expect in the future. In addition to KPIs such as revenue and return, the order value of the pipeline is one of the most important indicators of the success of the organization.
As with all software packages, the well-known law applies to CRM software: garbage in, garbage out. Database integrity and topicality, therefore, remain a continuous point of attention.
Think carefully about CRM KPIs. Too many metrics are counterproductive. Limiting the number of indicators you steer by makes it easier for teams to focus on them.
How do you select a CRM system?
As the world of Customer Relationship Management software has grown (and continues to grow), it can be difficult to select the right system for your business. You make a good software selection: based on a package of wishes and requirements and a framework of the budget, planning, type of organization, preference for technology, the current software architecture (other systems that are already in use), and other wishes.
Goal and relationship management strategy
It all starts with defining the goal. And in the current world of marketing and sales, it is very wise to do a broad inventory of the goals and wishes of the entire commercial team. Where previously relationship management software was often seen as a tool for sales, it is now often the basis for marketing, sales, account management (relationship management) and other disciplines.
In B2B marketing this is often very visible and Marketing and Sales work in tandem from the same CRM system. The objectives and wishes of all parties involved are therefore relevant when choosing a new CRM package.
Most CRM systems in the small business space offer free trials or are even free forever! Check out our article about free CRM systems.
CRM experts for guidance
Of course, you can also turn to a CRM expert to help you select a good system. These professionals have in-depth knowledge of available systems and capabilities. They work in a structured manner on the CRM selection so that you have carefully weighed all the options.
Social CRM Software
A trend in recent years is the rise of Social Media integration with CRM. Because customer relationship management revolves around knowing the customer, you see more and more information from the social media platforms in CRM systems. An example of Social CRM software is Nimble CRM.
Many CRM systems nowadays link with Linkedin to supplement profile information in the database or to show the latest activities of companies and contacts in the contact card. This can help salespeople, marketers, or service personnel interact with customers and prospects.
It is in any case common to integrate CRM software with other systems. For example, the software is often integrated with MS Office and email marketing software. CRM tools often offer options for sending mailings from the system.
eCRM; traditional vs modern?
A term that we see more often these days is eCRM. This is based on all interactions that are done online. We see eCRM more as a front-end and web-based solution aimed at capturing, analyzing, and using online interaction data.
Typically, we use the personalization of websites and clickstream analysis to make personalized offers. These CRM systems often also provide operational functions and, to a lesser extent, analytical capabilities. The basic idea does not differ much from the traditional Customer Relationship Management idea. Moreover, we see regular relationship management software continue to develop and you could say that the boundary between CRM, eCRM and Social CRM is becoming increasingly blurred.
When implementing CRM, what should you pay attention to?
Implementing a CRM system can be a daunting task, with many potential pitfalls along the way. Let’s explore the steps of a successful CRM implementation and highlight some of the common pitfalls to watch out for.
Step 1: Define Your Goals
Before implementing a CRM system, it’s crucial to define your goals for the system. What problems are you trying to solve? What improvements are you hoping to see? Defining clear goals will help you select the right CRM system and tailor its features to your business needs.
Pitfall: Failing to define clear goals can lead to choosing the wrong CRM system, implementing the wrong features, or neglecting critical business needs.
Step 2: Choose the Right CRM System
Choosing the right CRM system is a critical step in the implementation process. There are many CRM systems available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some systems are designed for small businesses, while others are geared toward large enterprises. When selecting a CRM system, consider factors such as pricing, features, customization options, and user-friendliness. Of course, you can be well informed through articles and tools on this website ;-).
Pitfall: Choosing the wrong CRM system can lead to wasted time, resources, and money. It’s crucial to thoroughly evaluate CRM systems before making a decision.
Step 3: Assemble Your Implementation Team
Implementing and using a new CRM solution is a team effort. It is crucial to have the right people in place . Your team should include stakeholders from all areas of the business, including sales, marketing, customer service, and IT. Your team should also include a project manager to oversee the implementation process and the rights people from the implementation partner.
Pitfall: Failing to assemble the right implementation team can lead to miscommunication, delays, and errors during the implementation process.
Step 4: Develop a Implementation (deployment) Plan
We have already discussed this at length on this site and cannot approach it enough: make sure you have a good deployment plan with a corresponding communication strategy.
Your plan should include a timeline, milestones, and tasks for each team member. It’s essential to be realistic about your timeline and to build in extra time for unexpected issues.
Pitfall: Failing to create a comprehensive implementation plan can lead to delays, missed milestones, and budget overruns.
Step 5: Clean Up Your Data
Before implementing a CRM system, it’s crucial to clean up your data. Strive for high CRM data quality. This involves reviewing and correcting any inaccuracies in your existing data, removing duplicate entries, and consolidating information from various sources.
Pitfall: Failing to clean up your data can lead to data errors, duplicates, and inconsistencies that can make it difficult to use the CRM system effectively.
Step 6: Customize Your CRM System
Once you have your data in order, it’s time to customize your CRM system. This involves tailoring the system’s features to your business needs, such as configuring workflows, creating custom fields, and setting up user roles.
Pitfall: Over-customizing your CRM system can lead to a complicated and confusing system that is difficult to use. It’s essential to strike a balance between customization and simplicity.

Step 7: Train Your Team
Implementing a CRM system is only half the battle; you also need to train your team on how to use it effectively. This involves providing comprehensive training on the system’s features, best practices for data entry and management, and any specific workflows or processes.
Pitfall: Failing to provide adequate training can lead to low adoption rates, data entry errors, and frustration among team members.
Step 8: Continuous Improvement
Finally, it’s essential to continually improve your CRM system to ensure that it meets the evolving needs of your business and your customers. This involves regularly reviewing your goals, and evaluating new features, technologies, and integrations. And, of course, retrieving and processing user feedback
Pitfall: Failing to prioritize continuous improvement can lead to a stagnant CRM system that fails to meet the needs of your business and your customers over time.
Read more about your CRM deployment plan in our comprehensive guide.
FAQ
The meaning of CRM concerns the structural management and strengthening of relationships.
CRM stands for Customer Relationship Management. People often talk about business software when it comes to Customer relationship management.
CRM software helps organizations to record, manage, and contact organizations.
Looking for a new CRM solution? Try our widget and make your CRM comparison.
